Get in Touch
Together, we can build smarter, more effective access solutions.
2.28.2025
by NexusHealth
Share this post


The healthcare landscape in the United States is poised for significant changes in 2025.
With a new administration in the White House and the anticipated confirmation of new heads of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and Food and Drug Administration (FDA), we expect the industry to continue evolving at a rapid pace, with changes in regulatory frameworks, advancements in innovation, and shifts in patient expectations shaping payer priorities. Payer organizations must adapt to these shifts while maintaining cost-effectiveness, quality of care, and operational efficiency.
This report by Nexus Health Group outlines 6 payer-focused trends to watch in 2025, helping organizations stay ahead in a complex, rapidly evolving, and competitive healthcare environment.
For this report, the Nexus team surveyed 17 payers, including pharmacy and medical directors. Plan sizes ranged from 500,000 to more than 5 million lives, with approximately 60% of payers representing over 5 million covered lives.
Trend 01
Oncology, CGT, and specialty drug spend remain top payer priorities in 2025.
When asked about the biggest priorities payers were facing moving into 2025, most are focused on specialty drug spend, with oncology drug spend, cell and gene therapies, and overall specialty drug spend as the top 3 priorities for 2025. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) management followed closely behind as a 2025 priority.

Trend 02
Payers are seeking better value for healthcare spend.
In 2025, decision-makers are confronting several critical challenges. Top concerns for payers included drug utilization and costs associated with trend and affordability. With rising healthcare costs, overall healthcare expenses are prompting payers to seek better value for healthcare dollars. GLP-1 management for obesity came in second as a top concern, especially as new options emerge, and the category continues to grow. Policy uncertainties filled out the list, with payers noting the impact of the IRA on Medicare, as well as the pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) regulatory environment as concerns for their organizations.
Trend 03
Management of key therapeutic areas will be a major focus for payers in 2025.
Payers are actively managing or considering management strategies for key therapeutic areas, each presenting unique challenges and opportunities.
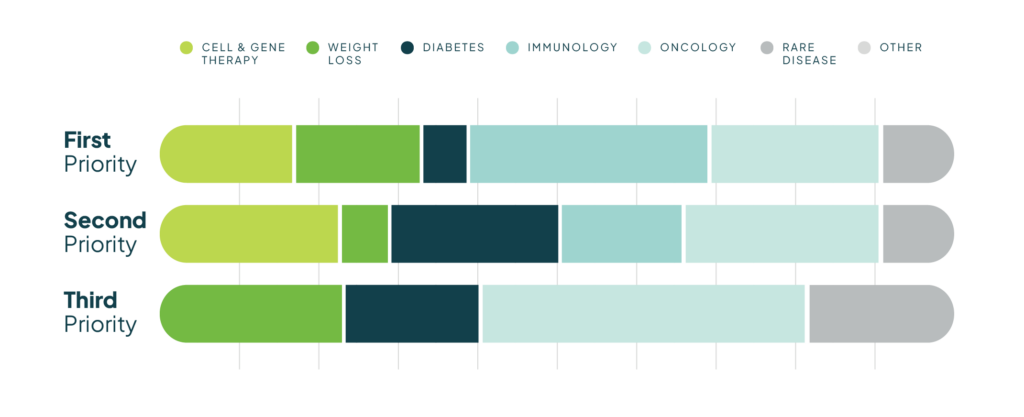
Immunology ranks as the top priority for management (29.4%), driven by the high total drug costs of systemic therapies for inflammatory diseases. As new treatment options emerge, payers remain focused on cost management in this growing category.
Oncology follows closely as a primary focus (23.5%), with an expanding pipeline of clinical trials, novel therapies—including gene and CAR T-cell therapies—and advanced diagnostics. Payers must assess the efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness of these innovations.
For the second most important management category, payers equally prioritized cell and gene therapies (23.5%), diabetes (23.5%), and oncology (23.5%). The rise of cell and gene therapies is reshaping treatment paradigms, but payers face challenges in balancing their long-term benefits with their high costs.
The third-ranked management priorities include oncology (31.1%), obesity/weight loss medications (23.5%), and diabetes (17.7%). The growing prevalence of obesity and metabolic disorders has increased the focus on GLP-1 agonists and other weight management therapies, requiring payers to assess their cost-effectiveness and overall impact on healthcare spending.
Notably, rare disease was ranked as a fourth-tier management priority, despite the increasing number of high-cost therapies in this space.
Trend 04
Formulary size will remain stable while maximizing savings & rebate revenue.
Within these priority therapeutic areas identified by payers, over 35% indicated that their management has increased compared to last year, while roughly 65% indicated that their management has remained the same.
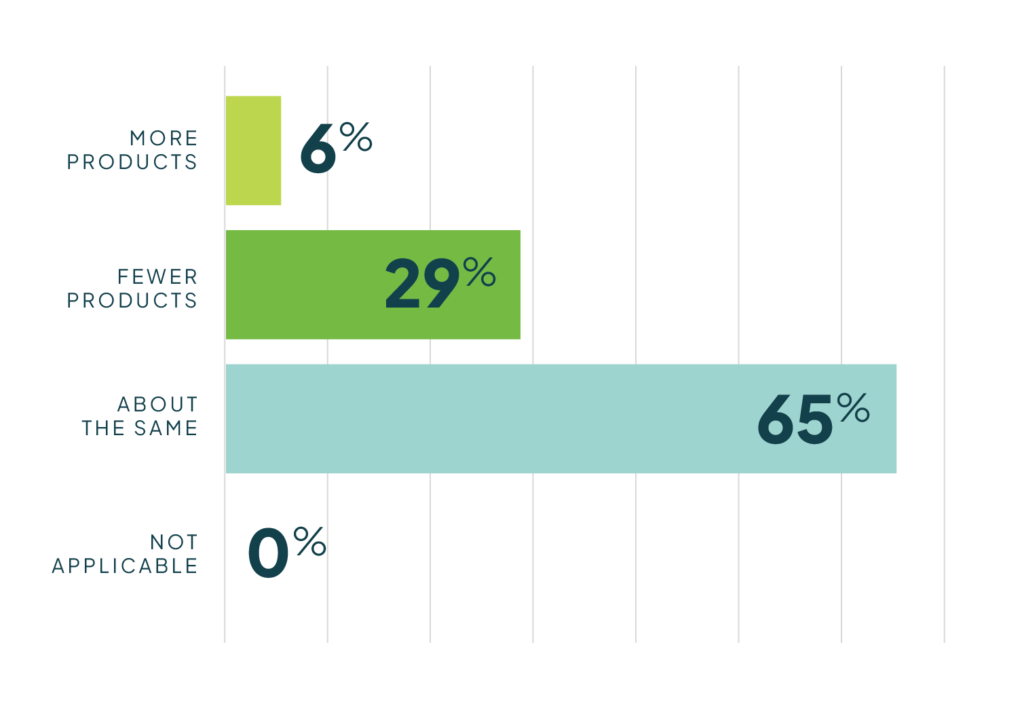
While many plans kept management unchanged, Medicare Part D formularies were expected to tighten due to increased payer liability in the catastrophic phase. Nearly 50% of plans covered fewer products this year, 30% maintained the same coverage, and none added more for 2025. The remaining 20% did not participate in Part D.

Commercial plan formularies generally covered about the same number of drugs in 2025 compared to 2024—65% indicated “about the same” coverage, compared to 30% who responded with coverage of “fewer products,” and 5% indicated that they increased coverage in 2025 compared to 2024.

In 2024, the FDA approved 50 new drugs, while multiple drugs lost patent protection, facing generic or biosimilar competition. With exclusivity losses and CMS-negotiated pricing, payers are expected to maintain formulary size,
maximizing savings from generic conversions while offsetting rebate revenue losses.1
Trend 05
Medical benefit management is on the rise, mirroring pharmacy benefit management.
Payers are applying pharmacy benefit management tactics to medical benefit drugs as the pipeline shifts toward provider-administered biologics. This trend is expected to grow as more plans adopt similar management strategies.

Seventy percent of plans surveyed indicated that they have a medical drug formulary in place. Among those plans with medical drug formularies,
the most common methods for managing these drugs include prior authorization (58%), followed by quantity limits (41%) and duration of treatment (11%). Plans are also using familiar strategies such as step therapy (58%) and copay/coinsurance differentiation (35%) to distinguish preferred from nonpreferred medical benefit drugs.
Payers employ various strategies to manage oncology drugs under the medical benefit, with all respondents indicating some level of oversight.
The most common approach is medical policy (76%), followed by guidelines (64%), step therapy for preferred products (58%), and pathways (52%). Of those using pathways, 47% rely on internal programs, while only 5% use an external vendor. Additionally, just 5% use an oncology benefit manager instead of internal management.
One IDN reported prioritizing generics and biosimilars when available and considering 340B pricing in preferred product selection.
Trend 06
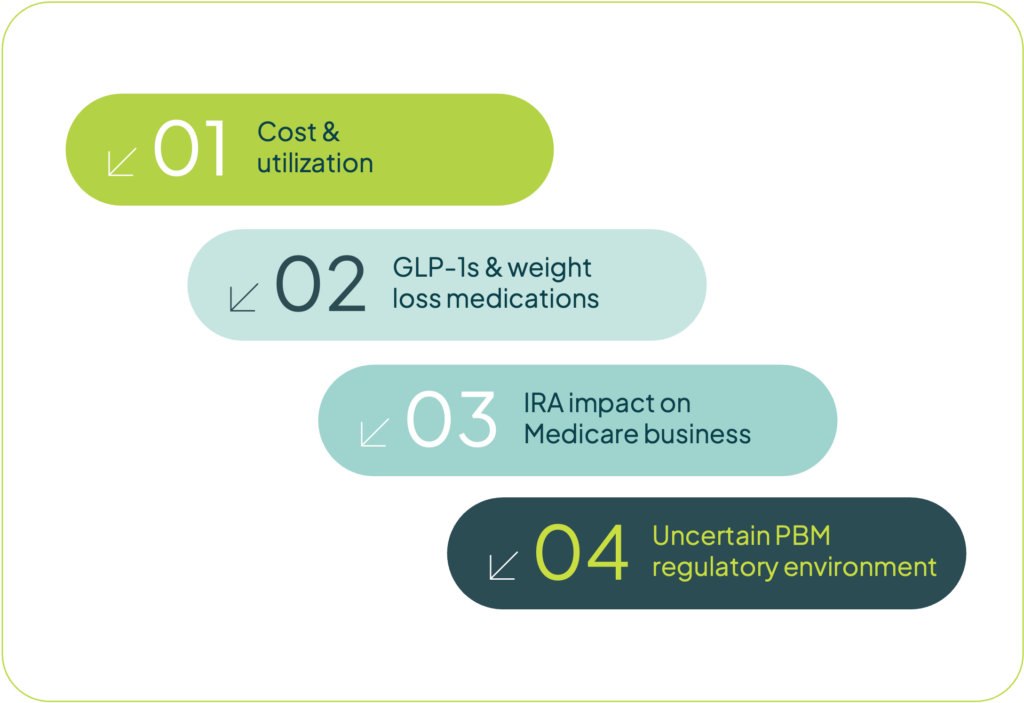
Government & industry uncertainties are what’s keeping payers up at night.
With the new administration, payers are preparing for five key themes.

About Nexus Health
The Nexus Health Group provides an integrated, simplified approach to comprehensive market access strategies, offering solutions in strategic
consulting, value communications, and patient access and affordability. Nexus experts combine deep market access experience in complex therapies with a foundation in science to provide the strategic advantages manufacturers need to launch and differentiate their products in today’s marketplace. Launched in 2025, Nexus may be a new company, but with an average of 21+ years of experience, the team is far from new to market access.
Meet the authors

ILENE AUERBACH, PhD
With over 20 years of experience in healthcare communications, Ilene has successfully launched and managed ongoing lifecycle initiatives for numerous pharmacy and medical benefit products to achieve market access and commercial goals. She is known for her diverse experience across stakeholders and therapeutic areas and is recognized for partnering with clients on innovative solutions grounded in science.

RYAN COX, RPh, MBA
Ryan’s insider knowledge as a former payer and more than 30 years of experience set him apart in the industry. Clients value his unique, real-world perspective on market access strategy, messaging, pull-through, and label expansions and rely on his formulary management, risk-based contracting, and deep therapeutic experience to meet access goals while optimizing utilization and reimbursement.